Minimum Requirements
For OpenShift Container Platform:
- 4 physical CPU cores
- 10.5 GB of free memory
- 35 GB of storage space
Here are the environment details I'm using:
- rj-codeready (10.20.10.119): 8vCPU, 16 GB RAM, 80 GB HDD1
- Rocky Linux 9.4
- Openshift version: 4.16.7
Required Software Package for Linux
# Fedora/Red Hat Enterprise Linux/CentOS
sudo dnf install NetworkManager# Debian/Ubuntu
sudo apt install qemu-kvm libvirt-daemon libvirt-daemon-system network-managerSetup & Start RedHat Openshift CodeReady
1. CRC will refuse to run as root, therefore you have to start the process as a regular user.
Ensure you're using a non-root user account, and then grant that user permission to manage systemd.
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/`id -u`
sudo systemctl restart systemd-logind.service
loginctl enable-linger rocky
export XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/$(id -u)2. Download crc binary. https://console.redhat.com/openshift/create/local
wget https://developers.redhat.com/content-gateway/rest/mirror/pub/openshift-v4/clients/crc/latest/crc-linux-amd64.tar.xz3. On Red Hat Enterprise Linux, assuming the archive is in the ~/Downloads directory, follow these steps:
- Extract the contents of the archive
- Create the
~/bindirectory if it does not exist and copy the crc executable to it - Add the
~/bindirectory to your$PATH
cd ~/Downloads
tar xvf crc-linux-amd64.tar.xz
mkdir -p ~/bin
cp ~/Downloads/crc-linux-*-amd64/crc ~/bin
export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin' >> ~/.bashrc4. Verify that the new crc executable is in use by checking its version:
$ crc version
CRC version: 2.41.0+e6495f
OpenShift version: 4.16.7
MicroShift version: 4.16.75. Configuring Usage Data Collection
# To manually enable telemetry, run the following command
crc config set consent-telemetry yes
# To manually disable telemetry, run the following command
crc config set consent-telemetry no6. Setting Up RedHat Openshift CodeReady
The crc setup command performs operations to set up the environment of your host machine for the Red Hat OpenShift Local instance.
The crc setup command creates the ~/.crc directory if it does not already exist.
Set up your host machine for Red Hat OpenShift CodeReady:
crc setup 7. Download the pull secret
Download the pull secret from the Pull Secret section of the CRC page on the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console and save it as pull-secret.json.

# pull-secret.json
{"auths":{"cloud.openshift.com":{"auth":XXXXXXXXXXXXX}}}8. Configuring the Instance (Optional)
Use the cpus and memory properties to configure the default number of vCPUs and amount of memory available to the Red Hat OpenShift Local instance, respectively.
Alternatively, the number of vCPUs and amount of memory can be assigned using the --cpus and --memory flags to the crc start command, respectively.
To configure the number of vCPUs available to the instance:
crc config set cpus <number>The default value for the cpus property is 4. The number of vCPUs to assign must be greater than or equal to the default.
To configure the memory available to the instance:
crc config set memory <number-in-mib>The default value for the memory property is 10752. The amount of memory to assign must be greater than or equal to the default.
9. Starting the Instance
Start the Red Hat OpenShift CodeReady with pull secret option
crc start --pull-secret-file ~/pull-secret.json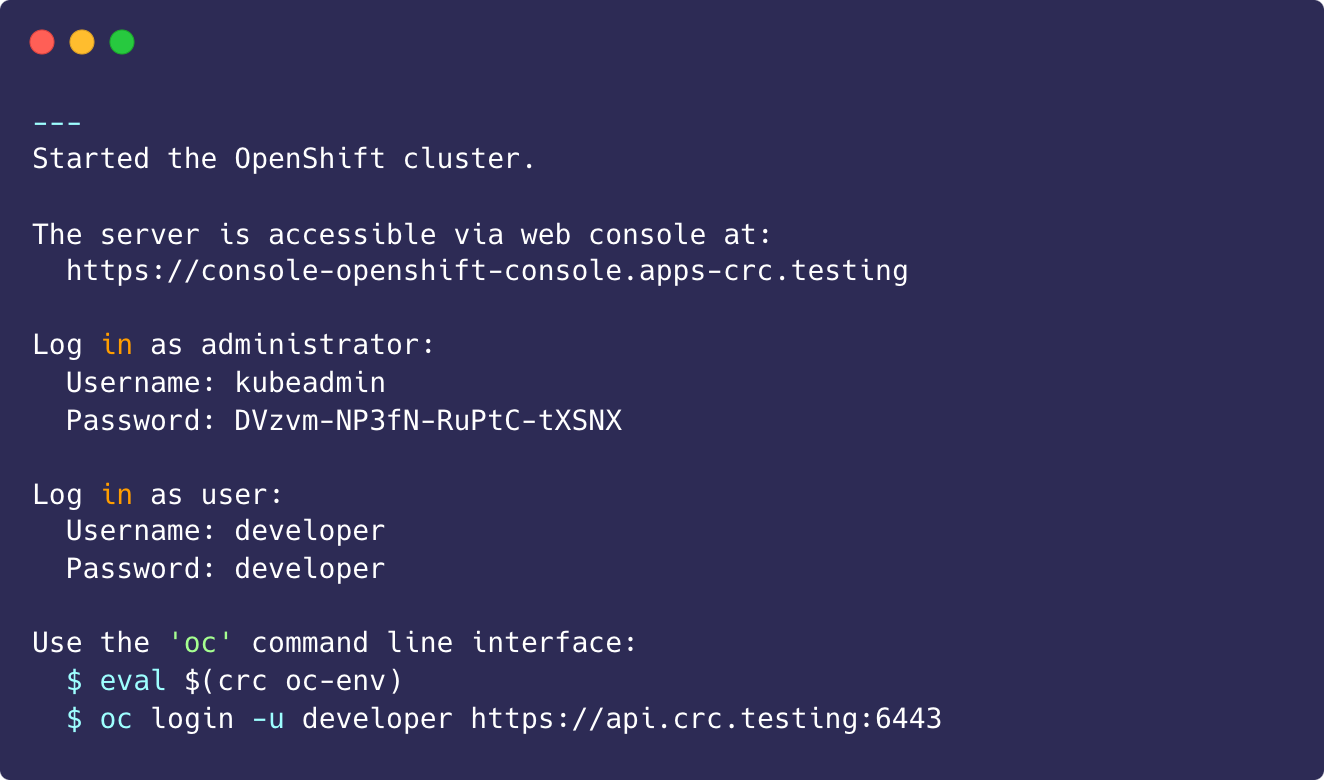
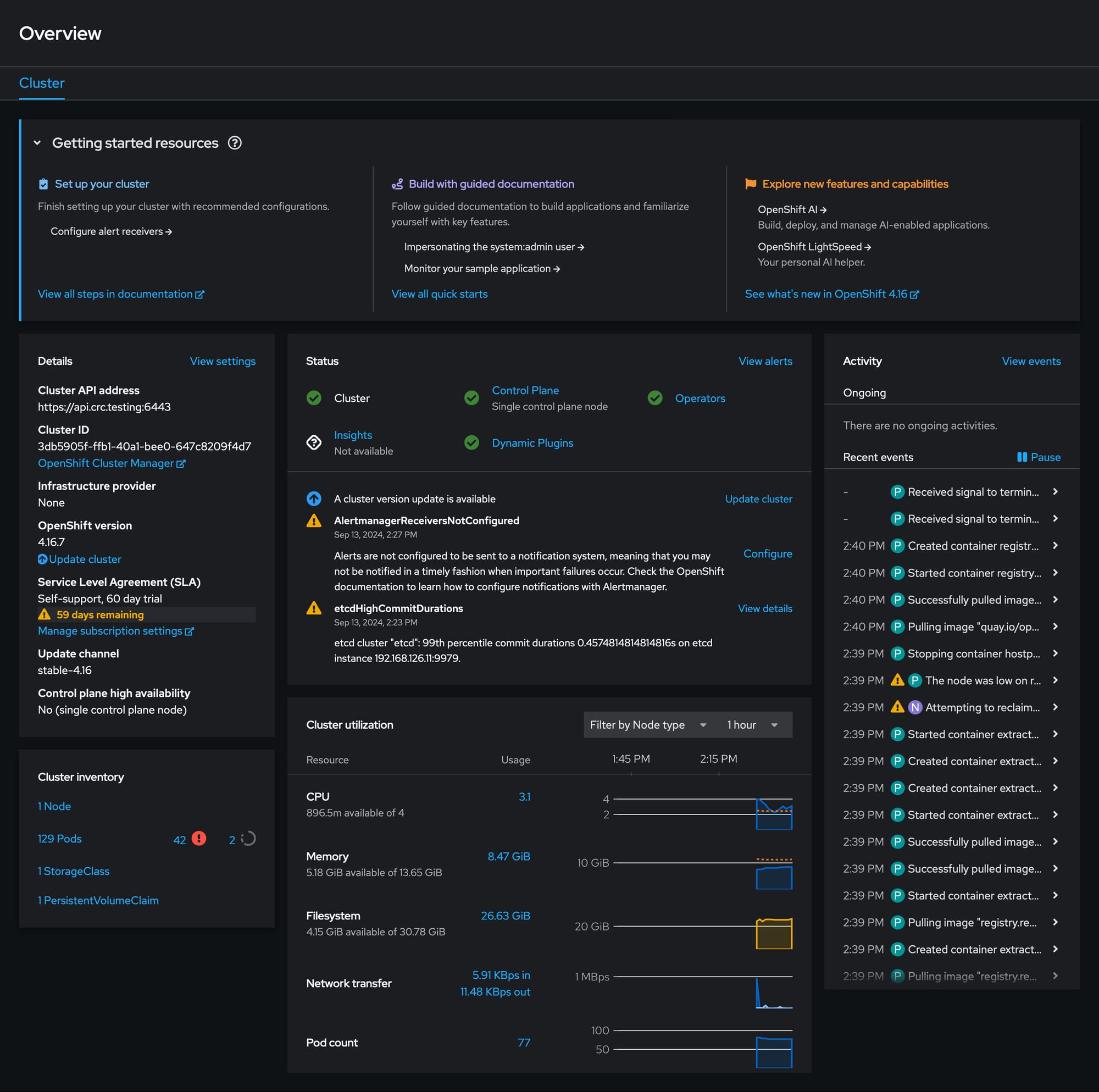
Accessing the Openshift web console
Access the cluster by using either the kubeadmin or developer user. Use the developer user for creating projects or OpenShift applications and for application deployment. Use the kubeadmin user only for administrative tasks such as creating new users or setting roles.
You can view the password for the developer and kubeadmin users by running the following command:
crc console --credentialsTo login as a regular user, run 'oc login -u developer -p developer https://api.crc.testing:6443'.
To login as an admin, run 'oc login -u kubeadmin -p DVzvm-NP3fN-RuPtC-tXSNX https://api.crc.testing:6443'

Accessing the OpenShift cluster with the OpenShift CLI
Access the OpenShift Container Platform cluster managed by Red Hat OpenShift Local by using the OpenShift CLI (oc).
1. Run the crc oc-env command to print the command needed to add the cached oc executable to your $PATH:
crc oc-env
eval $(crc oc-env)2. Log in as the developer user:
oc login -u developer https://api.crc.testing:6443Logged into "https://api.crc.testing:6443" as "developer" using existing credentials.
You don't have any projects. You can try to create a new project, by running
oc new-project <projectname>3. Log in as kubeadmin user:
oc login -u kubeadmin -p DVzvm-NP3fN-RuPtC-tXSNX https://api.crc.testing:6443Login successful.
You have access to 64 projects, the list has been suppressed. You can list all projects with 'oc projects'
Using project "default".4. You can now use oc to interact with your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. For example, to verify that the OpenShift Container Platform cluster Operators are available, log in as the kubeadmin user and run the following command
$ oc config use-context crc-admin
$ oc whoami
kubeadmin
$ oc get co
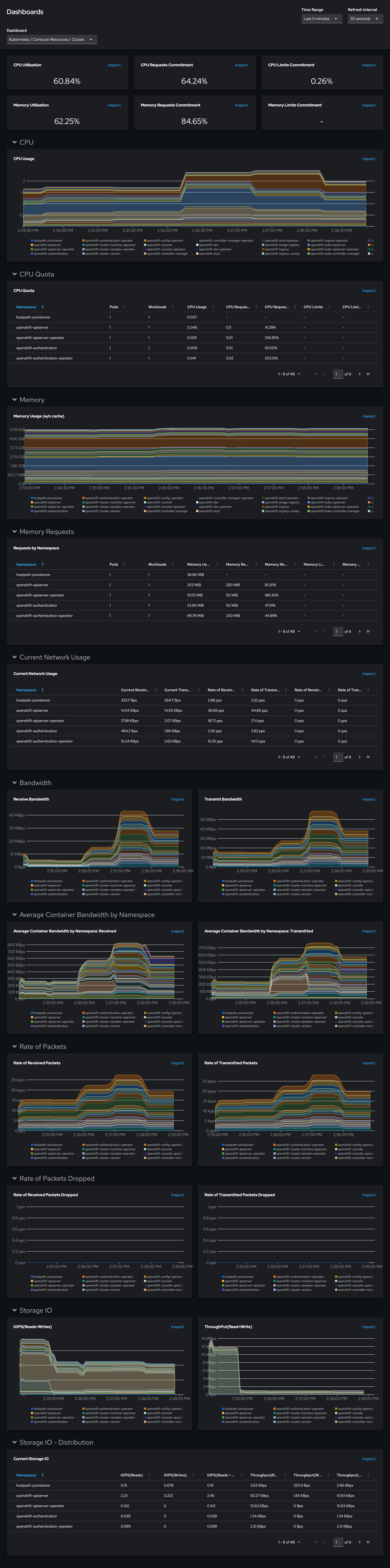
Enable Monitoring
Red Hat OpenShift Local disables cluster monitoring by default to ensure that Red Hat OpenShift Local can run on a typical notebook.
Prerequisites
1. Configure the memory available to the instance
crc config set memory 143362. Stopping the instance
crc stop3. Set the enable-cluster-monitoring configurable property to true
crc config set enable-cluster-monitoring true
4. To view the complete current configuration
crc config view- consent-telemetry : yes
- enable-cluster-monitoring : true
- memory : 143365. Start the Red Hat OpenShift CodeReady instance
crc startEnabling Override Operators
1. List unmanaged Operators and note the numeric index for the desired Operator
oc get clusterversion version -ojsonpath='{range .spec.overrides[*]}{.name}{"\n"}{end}' | nl -v 0
0 cluster-monitoring-operator
1 monitoring
2 cloud-credential-operator
3 cloud-credential
4 cluster-autoscaler-operator
5 cluster-autoscaler
6 cluster-cloud-controller-manager-operator
7 cloud-controller-manager2. Start the desired Operator using the identified numeric index
oc patch clusterversion/version --type='json' -p '[{"op":"remove", "path":"/spec/overrides/0"}]' -oyaml
3. Verify
oc project openshift-monitoring
oc get pods
4. Access Web Console